Construction, Real Estate, Infrastructure, Property And Hospitality Industry
The construction, real estate, infrastructure, property, and hospitality industries are rapidly evolving, driven by technological innovation, shifting consumer demands, and sustainability imperatives. Collectively, these sectors represent foundational elements of modern economies, supporting employment, investment, and urbanisation.
“It is not the beauty of the building you should look at: it’s the construction of the foundation that will stand the test of time.” — David Allen Coe
The global construction industry in 2024 is valued at over $13 trillion, accounting for about 13% of global GDP (McKinsey, 2024). Characterised by a wide range of activities, from residential buildings to large-scale infrastructure, this sector faces issues such as labour shortages, rising costs, and regulatory challenges. According to a report by McKinsey on construction productivity, labour productivity growth in the construction sector has averaged only 1% annually, significantly lagging behind other industries.
The construction industry is vital for global economic growth. It encompasses planning, design, construction, and maintenance of buildings and infrastructure. It focuses on sustainable practices, technological advancements like Building Information Modelling (BIM), and green materials. Challenges include labour shortages, fluctuating material costs, and regulatory issues, driving innovations in resource management. Growth is fueled by urbanisation, government infrastructure investments, and the demand for smart cities.
- Current Trends: The industry is increasingly embracing technologies like Building Information modelling (BIM) and AI-based predictive analytics to streamline project management and reduce delays. Robotics are also beginning to play a role, with autonomous machinery improving site safety and productivity.
- Challenges: Despite advancements, the construction sector struggles with fragmentation and a low rate of digital adoption. Labour shortages persist as a critical issue, with 75% of firms globally reporting difficulties in finding skilled labour (Deloitte, 2023). Additionally, the pressure to reduce carbon emissions is driving demand for sustainable materials and methods.
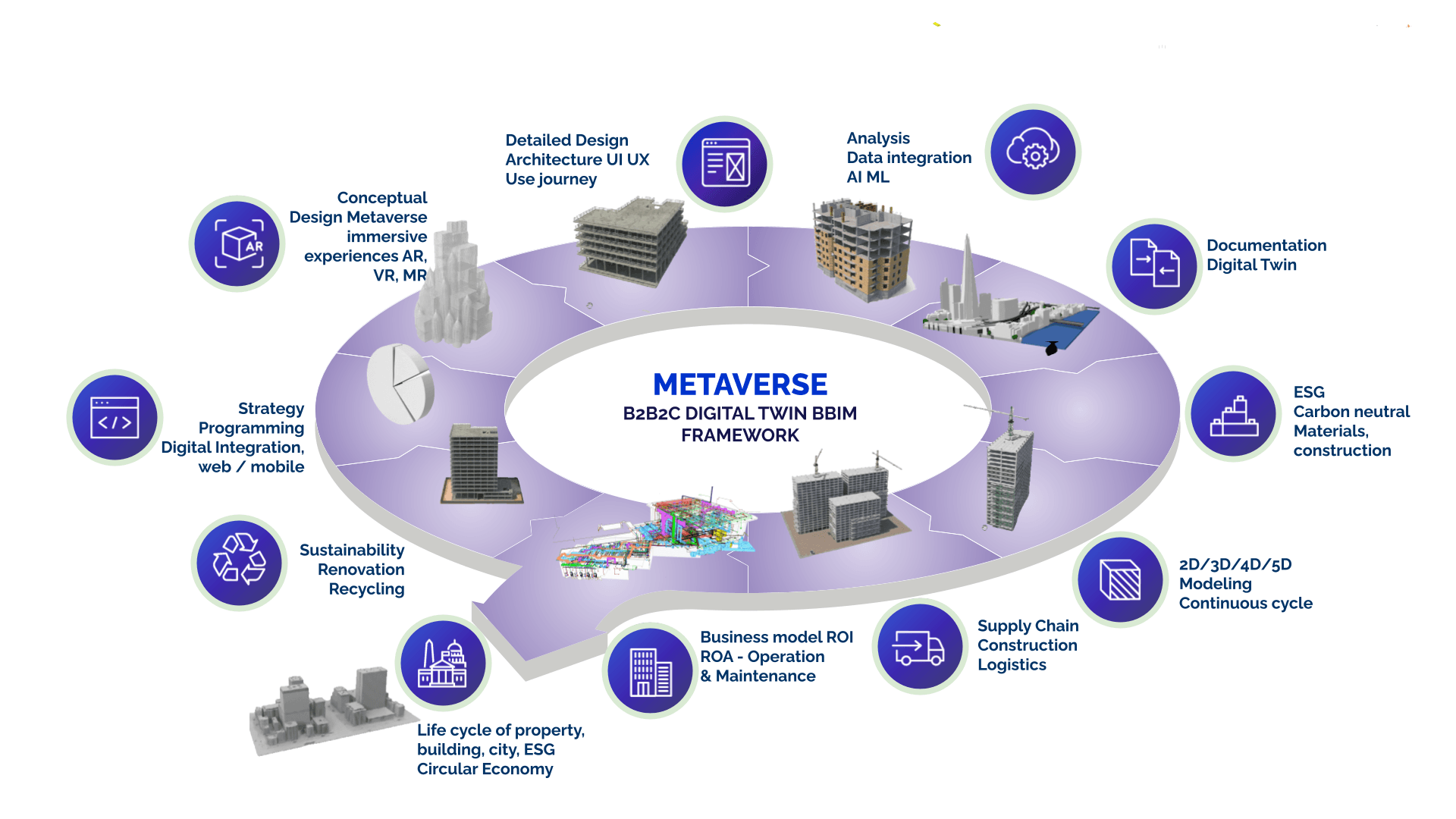
Real Estate Industry
Real estate, encompassing residential, commercial, and industrial properties, is an economic powerhouse. In 2024, the real Estate market worldwide is expected to reach a staggering value of US$634.90tn, largely driven by urbanisation and demographic shifts (Statista, 2024). The sector is marked by continuous innovation as smart building technologies and green building standards become the norm.
- Current Trends: Data-driven tools are enhancing property valuations, tenant management, and energy consumption optimisation. AI-driven real estate platforms are becoming increasingly popular, providing enhanced analytics and consumer insights. As Jones Lang LaSalle (JLL) notes, “the demand for sustainable and smart buildings has transformed the expectations of modern real estate development” (JLL, 2024).
- Challenges: The need to align with Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) standards has become a regulatory priority. Additionally, the rise of remote work has influenced demand for office space, while rising interest rates in certain regions have affected residential affordability and market stability.
Infrastructure Industry

Infrastructure is the backbone of economic activity, supporting everything from transportation to utilities and digital connectivity. With countries worldwide investing in infrastructure to promote economic resilience and urbanisation, Research by Oxford Economics and PWC projects that worldwide spending for infrastructure will exceed $9 trillion by 2025.
- Current Trends: Infrastructure projects are becoming more technologically advanced, leveraging digital twins and AI-driven models to predict wear-and-tear and optimise maintenance schedules. Initiatives to build smart infrastructure that integrates seamlessly with IoT technologies are also on the rise. For example, the European Union’s Green Deal includes digitalisation targets for its infrastructure projects to reduce emissions and improve operational efficiency (European Commission, 2024).
- Challenges: Infrastructure investments require substantial funding and long-term commitment, often leading to delays and budget overruns. Climate change and natural disasters also pose risks, prompting a shift toward resilient infrastructure designs that can withstand extreme weather.
Property Management Industry
The property management industry focuses on maintaining and enhancing the value of real estate assets. In 2024, this sector benefits from AI-powered solutions that simplify tenant management, optimise utilities, and improve overall building performance.
- Current Trends: Increasingly, property management firms are investing in smart building technology and automated systems that adjust lighting, HVAC, and security settings in real time based on occupancy and usage patterns.
- Challenges: With the rise of multi-use properties and complex regulations, property managers face pressures to maintain compliance while meeting tenant expectations for sustainability and comfort. Retrofitting older buildings with new technology is costly, yet essential for meeting modern standards and reducing environmental impact.
Hospitality Industry
The global hospitality industry, encompassing hotels, restaurants, and travel services, is a vibrant sector projected to grow from $4.67 trillion in 2023 to $4.99 trillion in 2024 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8%. Hospitality has undergone a profound shift post-pandemic, with a growing focus on digital customer experiences, health and safety standards, and eco-friendly practices.
- Current Trends: AI and data analytics play a central role in hospitality, from personalising guest experiences to predicting booking patterns and optimising room pricing. AI chatbots, for instance, assist with booking, check-ins, and customer support, enhancing guest satisfaction.
- Challenges: The industry faces a renewed focus on sustainability, with consumers increasingly opting for eco-friendly travel options. Labour shortages and high turnover rates remain persistent issues, compounded by inflationary pressures impacting operational costs.
Interconnections and Emerging Synergies
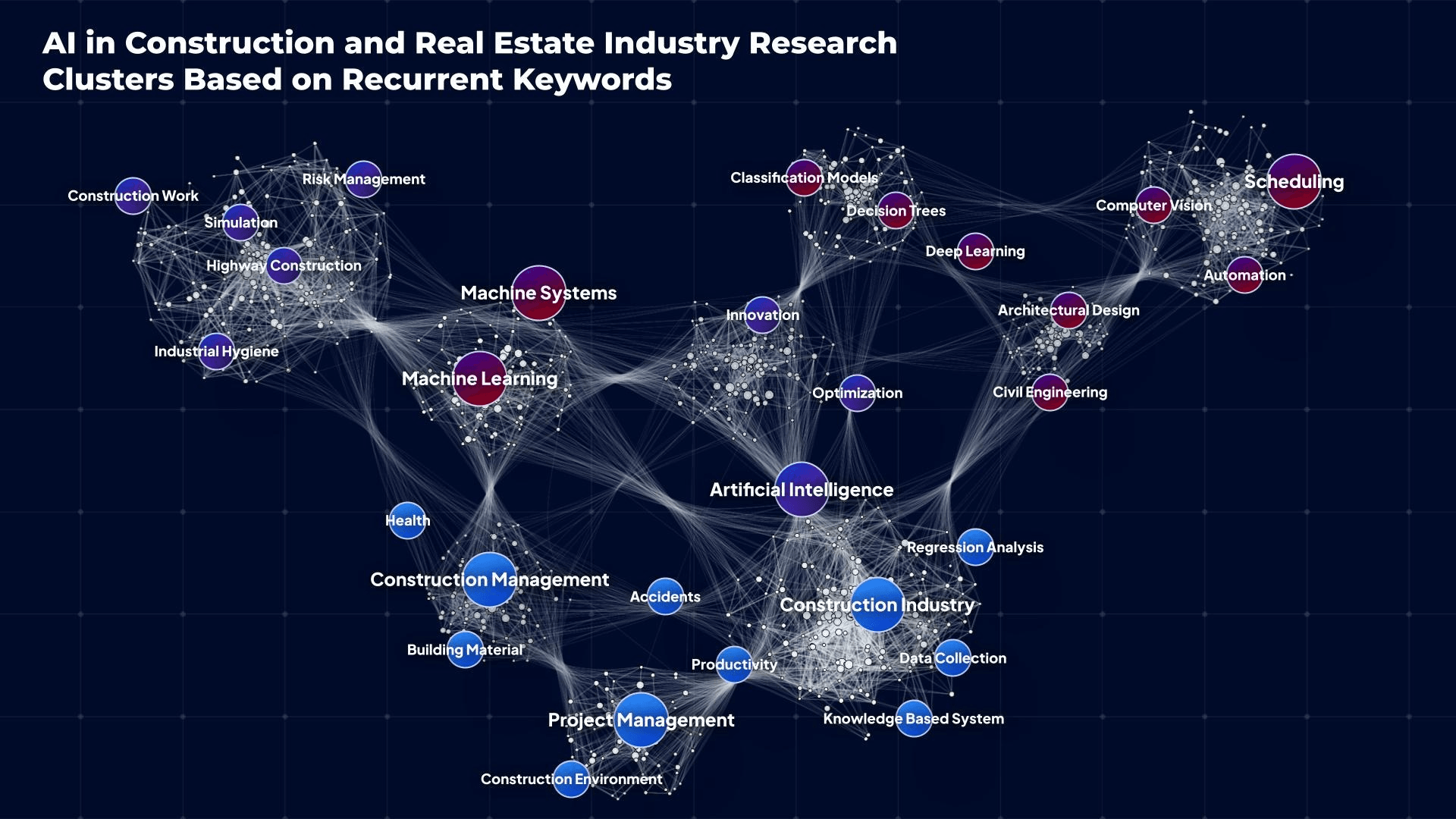
These industries do not operate in isolation but are deeply interconnected. For example, the growth of smart cities relies on advanced construction, real estate development, infrastructure, and hospitality services to create cohesive and livable environments. In 2024, the integration of AI across these sectors has created synergies, particularly in data sharing and smart urban planning. Collaborative initiatives—such as digital twin projects that enable cities to manage utilities, public spaces, and buildings in real-time—represent the future of a more integrated and intelligent urban landscape.
Opportunities
The construction, real estate, infrastructure, and hospitality sectors are poised to benefit from rapid urbanisation, projected to bring 68% to 70% of the global population into cities by 2050. This shift creates a demand for residential, commercial, and hospitality spaces, especially in emerging markets. Sustainable and smart city development represents a significant opportunity, as urban planners prioritise eco-friendly and technologically integrated spaces.
Adopting AI, blockchain, and IoT supports this vision by enhancing project management, transparency, and operational efficiency. For instance, AI’s predictive capabilities optimise resource allocation and minimise delays, while blockchain provides a secure framework for contracts and supply chain verification.
Moreover, sustainable construction, driven by consumer demand and regulatory pressure, opens doors to green building practices and energy-efficient designs. By investing in sustainable practices, firms gain a competitive edge, as buildings that meet standards like LEED or BREEAM attract eco-conscious investors and tenants.
Additionally, the industry can play a crucial role in achieving net-zero goals by 2050 through the development and implementation of essential projects, including renewable energy infrastructure, low-carbon activities, advanced building insulation, and other sustainability-focused initiatives.
The hospitality industry is also experiencing a resurgence post-pandemic, with a focus on personalised, data-driven guest experiences enabled by technology. IoT in hotels can create smart rooms that adjust to guest preferences, while AI-driven analytics help tailor offerings, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Challenges
Despite these opportunities, the industry faces several challenges. High technology adoption costs remain a barrier, particularly for smaller firms. Implementing AI, blockchain, or IoT solutions demands substantial upfront investment, and ongoing maintenance adds to the financial burden. In addition, the sector suffers from a shortage of skilled labour capable of navigating advanced digital tools, creating a need for reskilling initiatives.
Regulatory complexities also complicate innovation. Compliance with varying local and international regulations on data privacy, sustainable practices, and AI ethics is often costly and time-consuming.
The global supply chain volatility further adds pressure, as material shortages or delays can halt projects, increase costs, and reduce profitability. Environmental impacts remain a significant challenge too, as the industry is responsible for nearly 40% of global carbon emissions, driving the need for stricter sustainability practices.
While technology, sustainability, and urbanisation offer growth potential for construction, real estate, infrastructure, and hospitality, capitalising on these opportunities requires overcoming regulatory, financial, and environmental challenges
Conclusion
In 2024, the construction, real estate, infrastructure, property, and hospitality industries are evolving into a more interconnected ecosystem driven by technological advancements, sustainability goals, and consumer expectations. As each sector adopts AI and digital solutions, the potential for increased efficiency, resilience, and sustainable growth becomes evident.
By adapting to these transformations, industry leaders can build not only profitable but also adaptable and future-ready businesses, ensuring a lasting impact on the global economy and the environments we inhabit.
Read about The Size Of The Construction, Infrastructure, Real Estate, and Property Industry: https://www.dinisguarda.com/size-construction-infrastructure-real-estate-property-industry/
