AI And Taxes: Priority Use-Cases (Ranked by ROI & Feasibility)
Successful AI transformation in tax administration requires strategic prioritisation of use-cases based on return on investment, technical feasibility, and institutional readiness. Priority Use-Cases include AI-driven audit selection, real-time transaction analytics, revenue forecasting, casework copilots, and transfer pricing detection, creating a roadmap that ensures early wins and long-term capability building.
Artificial intelligence is reshaping how nations manage, collect, and enforce taxes, not as a distant vision, but as a present-day transformation unfolding across leading administrations. For decades, tax authorities have relied on manual audits, historical data, and periodic reporting systems to identify non-compliance.
Today, the integration of machine learning, automation, and advanced analytics is redefining that landscape, enabling governments to move from reactive enforcement to proactive intelligence. The shift is not simply technological; it’s structural. It represents a new paradigm of governance where data, algorithms, and institutional trust converge to create a fairer, more efficient fiscal ecosystem.
Yet, not all AI applications deliver equal value or feasibility. Some offer immediate, high-return improvements, such as predictive risk scoring or audit selection, while others, like network analytics or transfer pricing detection, demand long-term investment and technical maturity. Understanding where to begin and how to prioritise becomes the key differentiator between successful transformation and wasted potential.
Tier 1: Risk Scoring & Audit Selection
ROI: Very High | Feasibility: High | Timeline: 3-6 months
Audit selection represents the highest-impact application of AI in tax administration, directly determining how scarce enforcement resources are allocated across taxpayer populations. Current manual processes typically achieve audit hit rates of 40-60% in leading administrations. AI-enhanced systems can improve these rates to 80-90% whilst reducing selection time from weeks to hours.
Technical implementation combines supervised learning models trained on historical audit outcomes with feature engineering that captures compliance risk indicators from tax returns, third-party information, and business intelligence data. Gradient boosting machines, random forests, and neural networks with attention mechanisms deliver superior performance on structured tax data.
The mathematical impact scales multiplicatively across the entire audit programme. A large tax administration conducts 50,000 audits annually, with a current hit rate of 50%, and identifies 25,000 non-compliant cases. Improving hit rates to 80% would identify 40,000 cases, a 60% increase in enforcement effectiveness without additional human resources.
Feature importance analysis reveals key compliance risk indicators, including unusual deviations from industry benchmarks, timing patterns suggestive of income manipulation, expense ratios inconsistent with the business type, and network associations with known non-compliant entities. These insights improve both model performance and human understanding of compliance patterns.=
Explainability requirements can be entirely achieved through SHAP value decomposition and attention visualisation. Each audit selection includes clear attribution: “Selected due to: unusual profit margins (35% contribution), timing anomalies in expense reporting (25% contribution), network connections to high-risk entities (25% contribution), industry benchmark deviations (15% contribution).”
The IRS’s recent success with AI-enhanced selection of extensive partnership audits demonstrates the practical feasibility of this approach. Initial results show significantly higher collection rates per audit hour whilst reducing time from case identification to audit initiation.
Tier 2: Continuous Transaction Analytics
ROI: High | Feasibility: Medium-High | Timeline: 6-12 months
Real-time transaction monitoring transforms tax administration from retrospective investigation to proactive compliance management. This capability relies on e-invoicing or continuous transaction control systems, which provide near real-time visibility into economic activity.
Technical architecture requires stream processing capabilities handling millions of transactions daily. Apache Kafka manages data ingestion, Apache Spark provides distributed processing, and machine learning pipelines identify anomalous patterns using unsupervised learning, time-series analysis, and graph neural networks.
The value proposition centres on the early detection of compliance issues before they mature into significant problems. VAT carousel fraud, transfer pricing manipulation, and income underreporting become visible through pattern analysis that would be impossible with manual review methods.
Italy’s Sistema di Interscambio and Spain’s Suministro Inmediato de Información demonstrate operational feasibility at the national scale. These systems process over 3 billion invoices annually whilst providing real-time compliance monitoring and fraud detection capabilities.
The EU VAT gap reduction in countries with robust real-time reporting systems provides empirical evidence of effectiveness. Nations implementing comprehensive e-invoicing systems show VAT gaps 2-5 percentage points lower than those relying on traditional reporting methods.
Implementation challenges include managing data quality, reducing false positives, and integrating with existing case management systems. Success requires careful tuning of detection algorithms to strike a balance between sensitivity and operational workload management.
Tier 3: Revenue Forecasting & Policy Simulation
ROI: High | Feasibility: Medium | Timeline: 12-18 months
AI-enhanced revenue forecasting combines traditional econometric methods with machine learning techniques that capture nonlinear relationships, behavioural responses, and structural breaks in economic data. This capability provides government leaders with unprecedented insight into fiscal futures and policy impact assessment.
Technical implementation employs ensemble methods that combine multiple forecasting approaches: ARIMA models for baseline trends, machine learning models for nonlinear pattern recognition, and behavioural models for policy response estimation. Deep learning techniques handle high-dimensional data whilst maintaining interpretability through attention mechanisms.
Policy simulation extends forecasting into scenario analysis. Proposed changes to tax rates, bases, or compliance measures can be modelled using synthetic populations derived from actual taxpayer data. Monte Carlo simulation generates confidence intervals and sensitivity analysis for policy decisions.
The BRICS-plus research demonstrates superior performance of AI-enhanced forecasting during periods of economic volatility. Traditional models failed to capture rapid behavioural changes during COVID-19, whilst machine learning approaches adapted more quickly to new patterns.
Value delivery includes improved budget planning, better policy design, and enhanced economic management during crisis periods. Accurate revenue forecasting enables counter-cyclical fiscal policy, whilst policy simulation reduces unintended consequences from tax changes.
Implementation requires significant data science expertise and computational resources but delivers long-term strategic value through improved fiscal planning and policy design capabilities.
Tier 4: Casework Copilot Systems
ROI: Medium-High | Feasibility: High | Timeline: 6-12 months
AI assistants for tax administration staff handle routine information processing tasks whilst preserving human judgment for complex analysis. These systems excel at document summarisation, precedent retrieval, and initial case assessment whilst maintaining complete audit trails.
Technical architecture employs Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems combining vector databases of procedural knowledge with large language models fine-tuned on tax administration contexts. Enables natural language queries across vast repositories of legal precedents, administrative guidance, and case histories.
Practical applications include automatic case file summarisation, relevant precedent identification, drafting initial information requests, and compliance history analysis. These capabilities reduce administrative burden whilst improving case handling consistency and quality.
User experience design emphasises seamless integration with existing workflows rather than requiring significant operational changes. Chat interfaces, document annotation systems, and automated report generation provide immediate productivity improvements.
The value proposition addresses persistent challenges in complex case management, where individual cases may involve hundreds of documents, multiple legal precedents, and intricate factual patterns. AI copilots enable human experts to focus on analysis and judgment rather than information processing.
Risk management includes accuracy verification systems, bias detection in recommendations, and clear boundaries between AI assistance and human decision-making. Human oversight remains essential for all consequential decisions.
Tier 5: Internal Guidance Assistant
ROI: Medium | Feasibility: High | Timeline: 3-6 months
Knowledge management systems powered by AI provide staff with instant access to current legal guidance, administrative procedures, and technical resources. These systems serve both as training tools for new staff and reference resources for experienced practitioners.
Technical implementation requires a comprehensive knowledge base construction covering tax laws, regulations, administrative rulings, court decisions, and internal procedures. Graph databases model relationships between legal concepts, whilst vector search enables semantic query capabilities.
Currency management presents the primary technical challenge as legal frameworks evolve continuously through amendments, new rulings, and court decisions. Automated monitoring systems track updates whilst version control maintains historical accuracy.
Value delivery includes reduced training time for new staff, improved consistency in case handling, and democratised access to specialist knowledge across the organisation. Complex legal questions can be answered through natural language queries, rather than requiring specialist consultation.
Implementation focuses on user adoption through intuitive interfaces and integration with existing systems. Success depends on content quality and maintenance rather than algorithmic sophistication.
Tier 6: Network Analytics
ROI: Medium-High | Feasibility: Medium | Timeline: 18-24 months
Graph analytics reveal hidden relationships between taxpayers that indicate potential tax avoidance schemes, beneficial ownership structures, or coordinated non-compliance. These capabilities require sophisticated technical implementation but deliver high-value insights that are impossible to obtain through traditional analysis methods.
Technical architecture utilises graph neural networks, community detection algorithms, and anomaly identification systems that operate on comprehensive relationship datasets, including ownership structures, transaction patterns, and professional service connections.
Applications include beneficial ownership mapping for detecting corporate tax avoidance, identifying VAT carousel fraud, and analysing professional enabler networks. These insights support both case development and strategic enforcement planning.
Implementation challenges include data integration across multiple sources, computational complexity of graph algorithms at scale, and interpretation of complex network patterns by operational staff.
Tier 7: Transfer Pricing & BEPS Pre-screening
ROI: High | Feasibility: Low-Medium | Timeline: 24-36 months
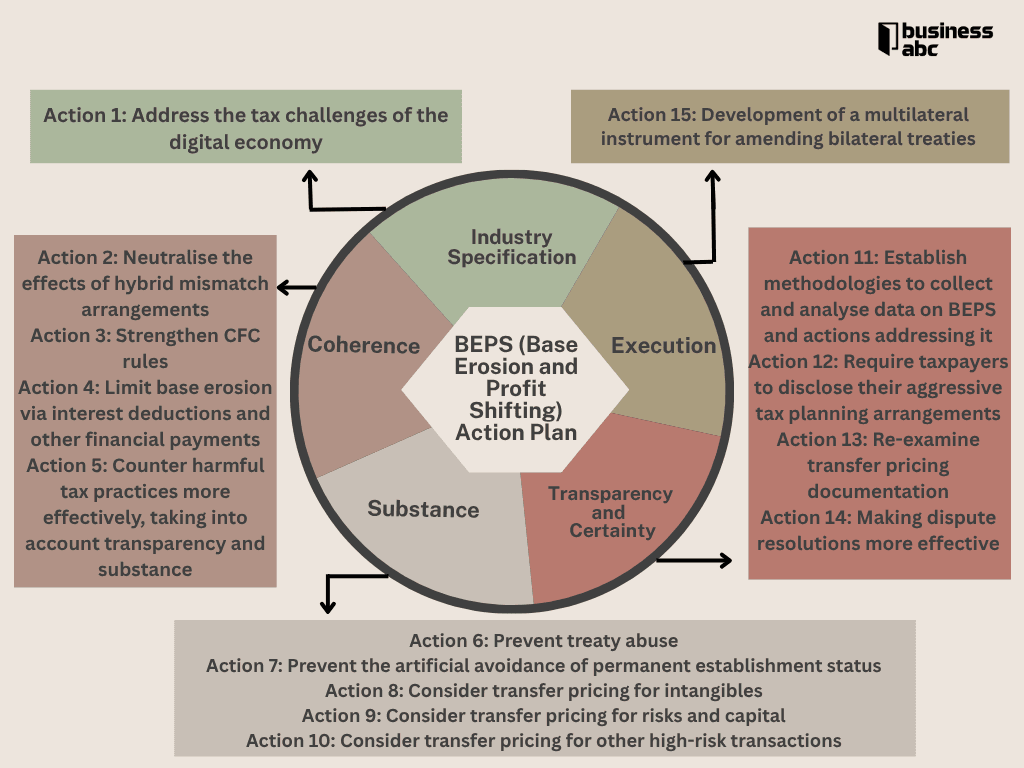
Advanced analytics for transfer pricing compliance and Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS) detection represent the most sophisticated analytical applications. Success requires deep technical expertise, comprehensive international data, and complex economic modelling capabilities.
Technical requirements include comparative analysis systems, economic benchmarking databases, and anomaly detection algorithms specifically designed for international tax planning schemes. Integration with international information exchange systems provides essential data inputs.
The value proposition centres on the early identification of aggressive tax planning structures before they mature into complex disputes requiring extensive audit resources. Automated screening enables risk-based allocation of specialist transfer pricing expertise.
The implementation timeline extends beyond the initial system deployment due to the complexity of international tax law, data availability challenges, and the requirement for specialist staff training in both technical and legal domains.
This tiered approach ensures that each implementation phase builds institutional capability whilst delivering measurable value. Early successes in risk scoring and transaction analytics lay the foundation for capabilities and stakeholder confidence, paving the way for more ambitious applications in network analysis and international tax compliance.
